Bitcoin Halving: A Deep Dive into the Scheduled Supply Shock of Bitcoin

Cryptocurrency
Understanding the Mechanics of Bitcoin Halving
The Bitcoin halving refers to a programmed event within the Bitcoin blockchain that cuts the reward for mining new blocks in half. This essentially reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins enter circulation. These halving events occur roughly every four years, or after every 210,000 blocks are mined. Let’s delve deeper;Mining
Bitcoin relies on a decentralized network of computers, or miners, to validate transactions and secure the network. Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles, and the successful miner receives a block reward in the form of newly minted Bitcoins.Controlled Supply
Unlike traditional fiat currencies, Bitcoin has a predetermined maximum supply of 21 million coins. This finite supply is a core principle behind Bitcoin’s design, aiming to prevent inflation and maintain its value over time.The Halving Schedule
Bitcoin halving is a built-in mechanism to gradually slow down the issuance of new Bitcoins. Every 210,000 blocks (approximately four years), the block reward is cut in half. Here’s a historical timeline of Bitcoin halving events:- Block 210,000 (November 28, 2012): Block reward reduced from 50 BTC to 25 BTC.
- Block 630,000 (July 9, 2016): Block reward reduced from 25 BTC to 12.5 BTC.
- Block 1,260,000 (May 11, 2020): Block reward reduced from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC.
- The next halving is projected to occur around April 2024, bringing the block reward down to 3.125 BTC.
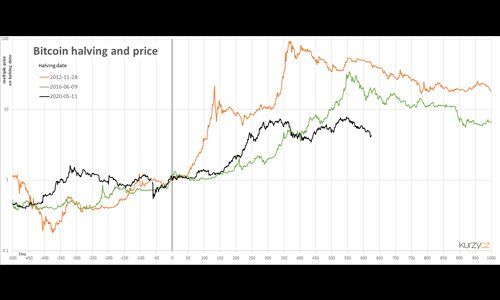 Image Source: wikipedia.org
Image Source: wikipedia.org
The Potential Impact of Bitcoin Halving on Price
The theory behind the halving’s impact on price is rooted in basic principles of supply and demand. By reducing the rate at which new Bitcoins are created, the halving restricts supply. If demand for Bitcoin remains stable or increases, then the price could potentially rise due to this constrained supply.Historical Performance
Following each halving event, Bitcoin’s price has experienced significant surges. However, it’s important to note that correlation doesn’t necessarily imply causation. Other market factors can also influence Bitcoin’s price movements.Post-Halving Price Rises
While not a guaranteed outcome, there seems to be a historical trend of Bitcoin’s price rising after each halving event. This could be due to multiple factors, including increased media attention, investor anticipation, and the aforementioned supply and demand dynamics.Market Volatility
The cryptocurrency market is known for its volatility. The price of Bitcoin can fluctuate significantly due to various factors, and the halving event itself can introduce a period of uncertainty.Future Implications
It’s challenging to predict the exact impact of the upcoming halving (expected in April 2024) on Bitcoin’s price. However, understanding the halving’s role in limiting supply can be a valuable tool for cryptocurrency investors and enthusiasts.Beyond Price: Other Considerations of Bitcoin Halving
The halving’s influence extends beyond just impacting Bitcoin’s price. Here are some additional considerations:Impact on Miners
With reduced block rewards, miners will earn less Bitcoin for their computational efforts. This might incentivize miners to become more efficient or encourage consolidation within the mining industry.Network Security
Mining rewards also serve as an incentive for miners to secure the Bitcoin network. The halving could potentially lead to increased competition among miners, ultimately strengthening the network’s security.Long-Term Sustainability
As the block reward approaches zero over time (with the final halving estimated to occur around the year 2140), transaction fees are expected to become the primary source of revenue for miners. This shift raises questions about the long-term economic sustainability of the Bitcoin mining model.Bitcoin Halving – A Scheduled Event with Far-Reaching Effects
The Bitcoin halving is a significant event built into the very fabric of Bitcoin’s design. By limiting the issuance of new coins, the halving plays a crucial role in maintaining Bitcoin’s scarcity and potentially influencing its price. However, the halving’s impact goes beyond just price movements. It can affect the profitability of mining, influence network security, and raise questions about the long-term sustainability of the Bitcoin mining model. As the next halving approaches in April 2024, staying informed about this critical event can be beneficial for anyone interested in Bitcoin and the cryptocurrency market as a whole. By understanding the mechanics, historical impact, and potential future implications of the halving, investors and enthusiasts can make more informed decisions in this ever-evolving digital landscape.You Might Be Interested In:
- Beyond Likes and Followers: Exploring the Evolving Landscape of Social Media
- Is TikTok Facing a US Ban? Decoding the New Law and Its Impact on Millions of Users
- Click, Buy, Pollute? Environmental Impact of Online Shopping and Ways for Sustainable E-commerce
- The High Price of Crypto: Environmental Cost of Mining and Solutions for a Greener Future
Frequently Asked Questions?

01
Cybersecurity
Beyond Likes and Followers: Exploring the Evolving Landscape of Social Media
Apr 28, 2024
01
Tech news
Is TikTok Facing a US Ban? Decoding the New Law and Its Impact on Millions of Users
Apr 27, 2024

01
Tech news
Click, Buy, Pollute? Environmental Impact of Online Shopping and Ways for Sustainable E-commerce
Apr 26, 2024

01
AI & ML
Gemini Evolves: Your AI Assistant on the Go with the New Overlay Feature
Apr 24, 2024
SUSBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Join our subscribers list to get the latest news and special offers.
Beyond Likes and Followers: Exploring the Evolving Landscape of Social Media
Is TikTok Facing a US Ban? Decoding the New Law and Its Impact on Millions of Users
Click, Buy, Pollute? Environmental Impact of Online Shopping and Ways for Sustainable E-commerce
The High Price of Crypto: Environmental Cost of Mining and Solutions for a Greener Future